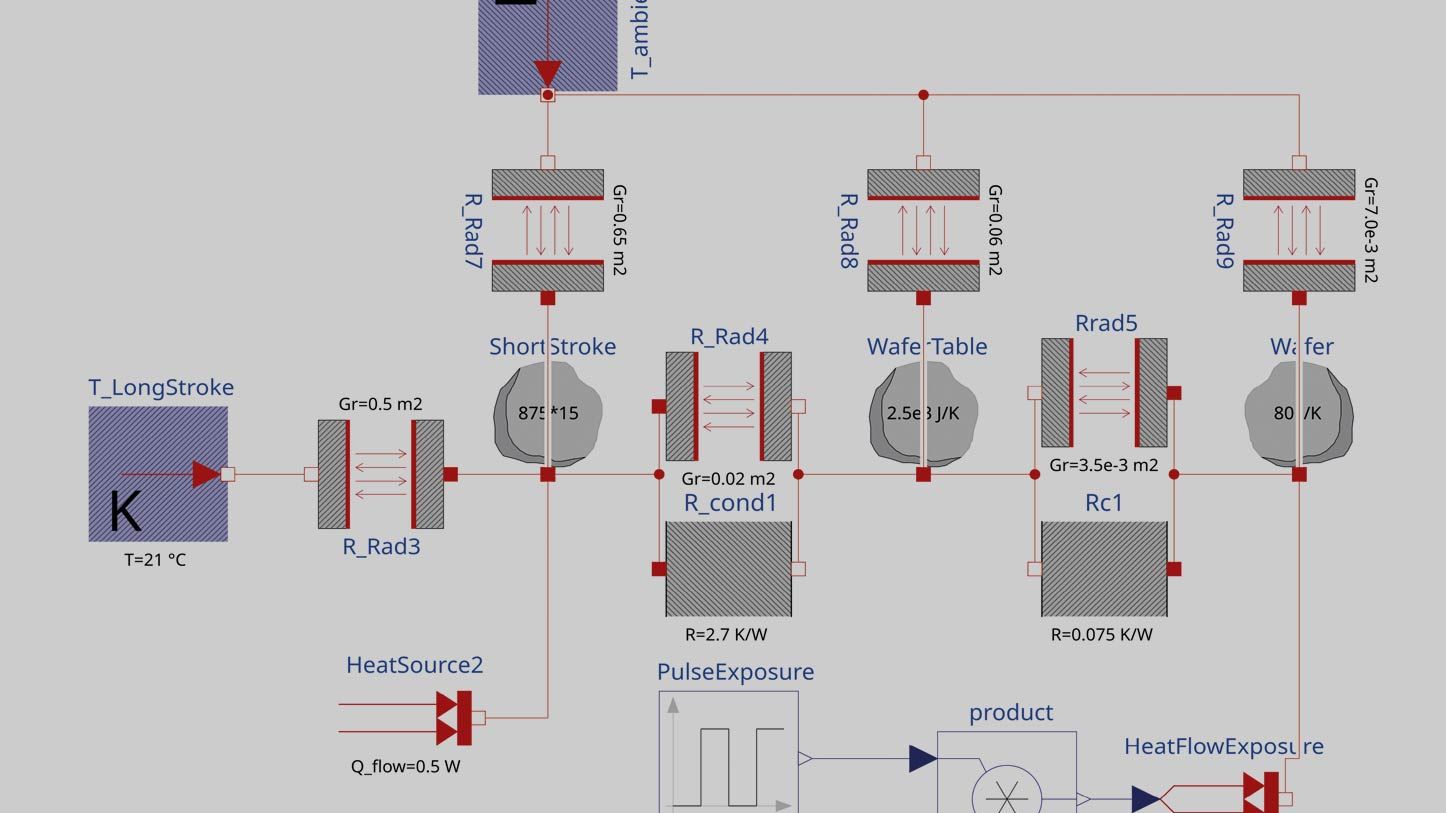
LEM and FEM modelling are useful methods for predicting thermal behavior and evaluating strategies to mitigate thermal drift in high-precision engineering systems such as long-stroke and short-stroke actuators of wafer stages. In the article, it is shown in detail how both methods can be applied to the mirror block of a wafer stage. LEM modelling is often employed to model thermal behaviour of complex systems, as it allows for fast and relatively easy modelling of transient heating and cooling problems. If temperature differences within components are not negligible, then the use of spatial discretisation methods such as FEM is necessary, which is computationally much more expensive but can provide the level of detail that is required.
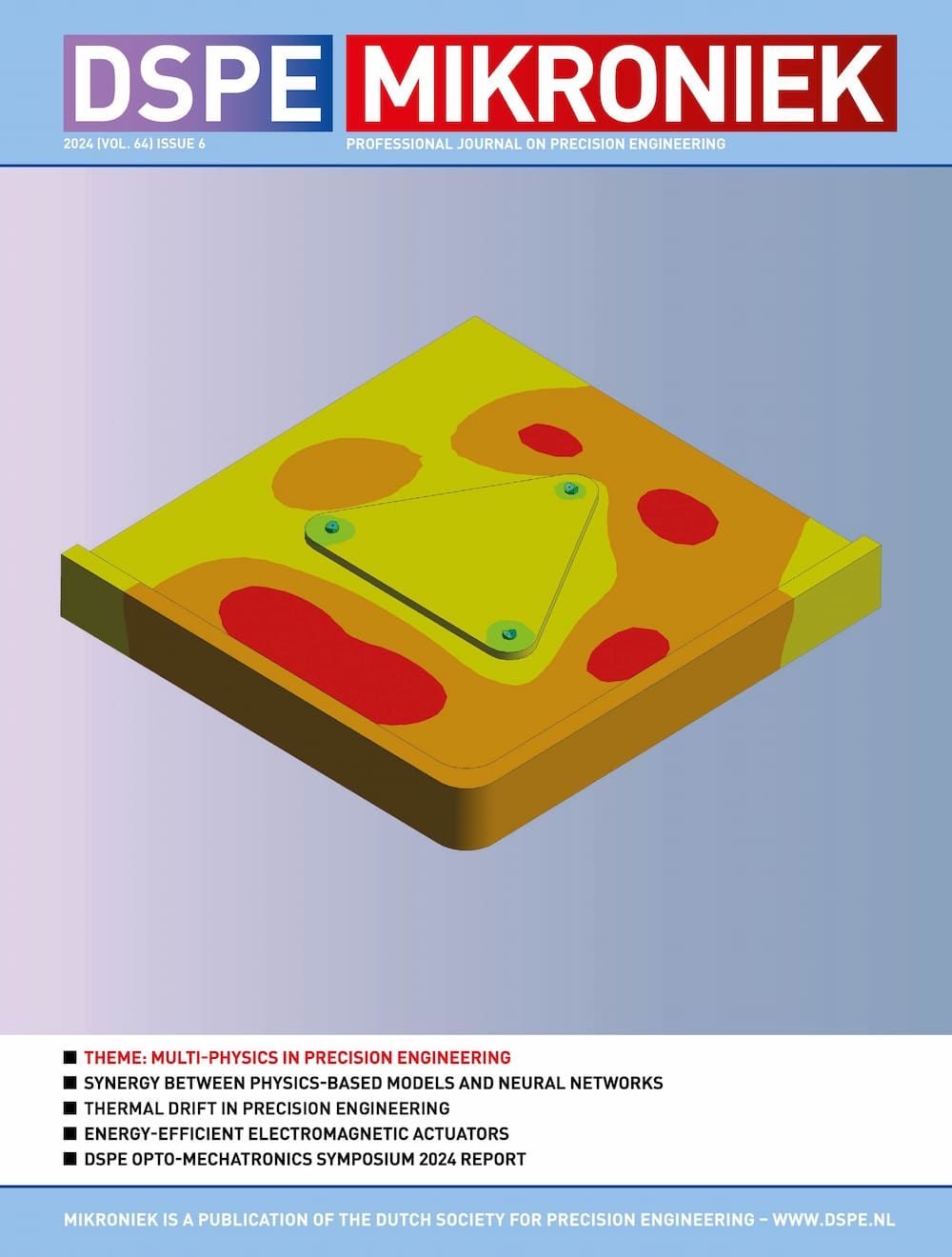
The image on the cover shows a non-uniform temperature distribution in a mirror block of a wafer stage, as a result of thermal dissipation induced by eddy currents in the magnets attached to the bottom. The flatness of the mirror planes can be distorted because of the uneven thermal expansion.
Read the full article here.